Shoulder Anatomy
The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body, which makes it more prone to instability and injury.
Bones
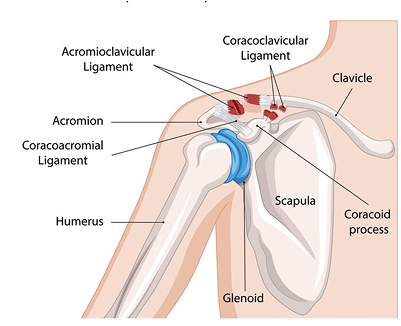
The shoulder is a joint that is shaped like a ball-and-socket. At the top of the upper arm bone, which is called the humerus, there is a rounded part that fits into a small socket known as the glenoid. This socket is located on the shoulder blade, which is also called the scapula. The shoulder joint is made where three bones come together: the collarbone (clavicle), the shoulder blade (scapula), and the upper arm bone (humerus).
Humerus
The attachment is made to the muscles located in the upper arm. The humeral head forms the rounded portion of the ball-and-socket shoulder joint.
Scapula
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is a flat, triangular-shaped bone that serves as an attachment point for the muscles in the back and neck.
Clavicle
The clavicle is an S-shaped bone that links the shoulder girdle to the body trunk. It helps keep the shoulder in a proper position relative to the spine and allows for different arm movements during physical activities. Besides offering structural support, the clavicle also shields key nerves and blood vessels that travel from the neck to the armpit area.
Coracoid Process
The coracoid process is the bony projection located near the front of the shoulder joint, and it is involved in handling varus forces.
Acromion
The acromion is an extension of the scapula, which is the shoulder blade, that extends around the shoulder joint at the back to form a type of roof. This feature is also referred to as the acromial process.
Glenoid
The glenoid is a shallow depression found at the tip of the scapula, forming the socket portion of the ball-and-socket joint in the shoulder.
Soft Tissue
Rotator Cuff
These tendons help keep the arm securely within the shoulder joint. A significant number of shoulder issues result from injuries to the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff is made up of four tendons that link four muscles in the shoulder to the upper arm bone, which is called the humerus.
Biceps Tendons
The biceps tendon is a long, cord-like structure that connects the biceps muscle to the shoulder and plays a role in stabilizing the joint.
Caracoclavicular Ligament
Ligaments are structures that connect bones to each other, and specifically, the coracoclavicular ligament connects the coracoid process of the scapula to the clavicle.
Acromioclavicular Ligament
Ligaments are structures that connect one bone to another, and the acromioclavicular ligament specifically connects the acromion process to the clavicle.
Glenoid Labrum
The Glenoid labrum is a ring made of fibrous cartilage that surrounds the glenoid, helping to keep the shoulder joint stable.
Articular Cartilage or the capsule
The capsule around the shoulder joint is a strong ligament that assists in maintaining the normal alignment of the ball and socket.
Movements
- Forward Flexion: The arm is stretched forward in front of the body, with the palm facing downward and raised to its maximum height.
- Abduction The straight arm is raised at the side, with the palm down, as high as possible.
- External Rotation: The elbows are positioned on either side of the body, bent at a 90-degree angle with the palms facing each other. While maintaining contact of the elbows with the body, the hands are moved outward as far as possible.
- Internal Rotation: The arm is positioned behind the back with the elbow bent. The individual extends their arm as high up the back as they can reach. The distance is measured from a particular point on the spine.